Japan
Wood Products Prices
Dollar Exchange Rates of 10th
March
2019
Japan Yen 111.16
Reports From Japan
¡¡
Major economic indicator dips for
third month
Private-sector machinery orders fell over 5% in January
from the previous month according to the latest news from
the Cabinet Office. The trend in machinery orders is an
indicator of capital expenditure by Japanese companies
and as such reflects business prospects.
The January decline in orders was the third consecutive
monthly decline.
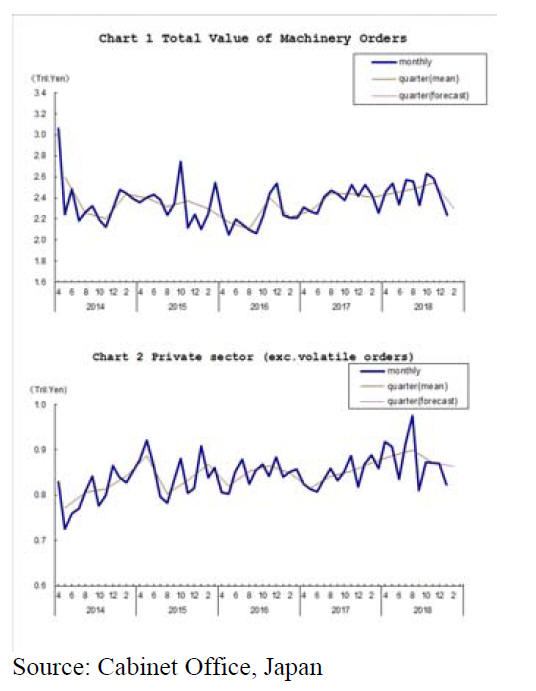
Economy into reverse once again
In a reversal of its earlier claim that the Japanese economy
the country had enjoyed six years and two months of
sustained growth, the longest since the end of World War
II now the Cabinet Office has downgraded its assessment
saying the economy has been in negative growth since the
end of 2018 signalling a technical recession.
It now seems that Japan¡¯s economic expansion may have
peaked several months before January. The main reason
for the abrupt change is the slowdown of the Chinese
economy which is having a heavy impact on Japan and has
resulted in the government downgrading its assessment
of industrial output for the first time in more than three
years.
Workers likely to see smaller pay rise this year
Rengo, The Japanese Trade Union Confederation and
most unions have been calling for increases in base pay in
negotiations with employers. Rengo demanded a further
2% increase in base which, if accepted would be the fourth
consecutive year of increases but the employers are in no
mood to agree it appears.
In an interview the head of the Japan Business Federation
(Keidanren) said the government should avoid trying to be
specific on how much companies should raise wages.
Companies have increased wage hikes in each of the past
three years but this has never been at a level considered
necessary to drive up inflation.
Higher pay for workers has been a key part of the
government¡¯s economic growth strategy which is based on
the philosophy that improved pay will lift consumption
and drive prices higher but this has not proven very
successful so far and with the prospects of a consumption
tax rise later this year prospects for boosting consumption
have dimmed.
See:
https://www.japantimes.co.jp/news/2019/03/11/business/japaninc-
push-back-workers-can-expect-smaller-raisesyear/#.
XIYZUYYzbIU
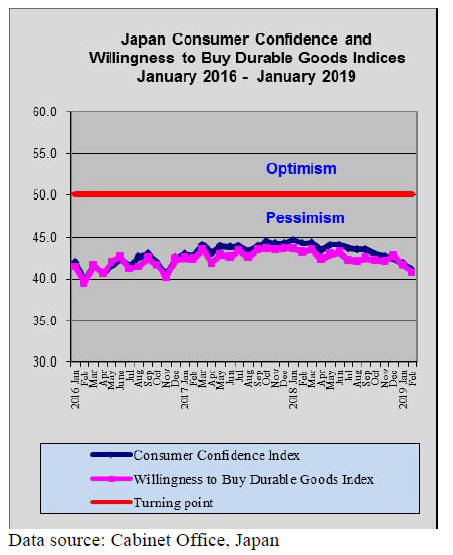
Consumer confidence suffers triple whammy
Consumer confidence in Japan continues to weaken and
the index released by the Cabinet Office shows confidence
and willing ness to buy durable goods such a furniture at
the lowest level since November 2016.
This underlines the sentiment of both consumers and
manufactures regarding prospects for the Japanese
economy at a time when tough trade talks with the US are
about to begin, economic growth in China has slowed
driving down imports from Japan and the likelihood that
the consumption tax will be raised in October this year.
See: https://www.esri.cao.go.jp/en/stat/shouhi/shouhi-e.html
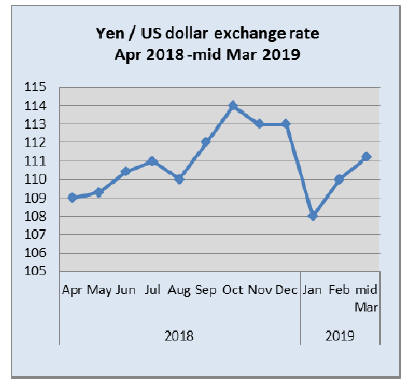
US pushes for currency clause in trade
negotiations
In early March the Japanese yen strengthened against the
US dollar despite the recessionary news.
This raised the alarm in the Bank of Japan (BoJ) which
immediately called for additional stimulus should growth
stall even further. Comments from the BoJ have
complicated the build up to trade talks with the US which
is asking that a currency clause be included in any trade
agreement with Japan.
But the government is opposed to this claiming the
correlation between the yen¡¯s exchange rate and exports
has weakened significantly since the global financial
crisis. But the US side is remaining firm on this having
already secured such an arrangement in the trade pacts
with Canada and Mexico and is said to be seeking one
from China.
See:
https://www.japantimes.co.jp/news/2019/03/06/business/econom
y-business/japan-stresses-weak-link-strength-yen-exports-aheadu-
s-trade-talks/#.XIYYxYYzbIU
Lest we forget
March 11th 2019 marked eight years since a massive
magnitude 9 earthquake struck Eastern Japan. The
Japanese media reported that, as of 11 March this year,
over 50,000 people still remain displaced from their homes
destroyed by the tsunami triggered by the earthquake or
forced to evacuate after the explosion and release of
radiation when workers at the nuclear plant in the region
were unable to secure the reactors during the crisis which
led to a core meltdown.
The number of people killed directly or indirectly by the
disaster and those missing and feared dead, is 22,131,
according to the National Police Agency.
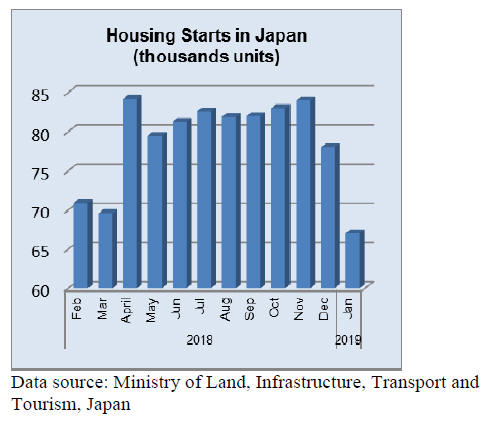
Efforts to avoid rush-to-buy before October tax
increase
The Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport will
launch a scheme to reward those buying or renovating a
home before the planned increase in consumption tax in
October this year. More information can be found in the
Japan Lumber Report extracts on page 14.
Wooden door imports
The value of Japan¡¯s January imports of wooden doors
(HS 441820) were little changed from January 2018 but
compared to December 2018 there was a 10% increase in
the value of imports.
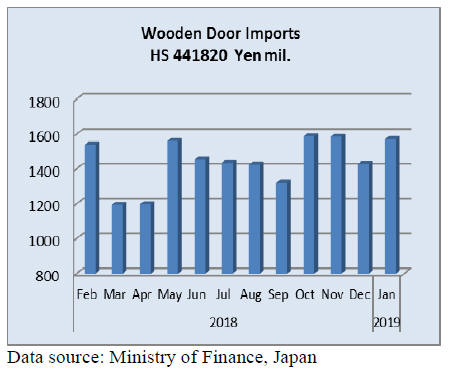
Four supply countries accounted for around 90% of
all
Japan¡¯s wooden door imports, China (60%), Philippines
(18%), Indonesia (7%) and Malaysia (5%).
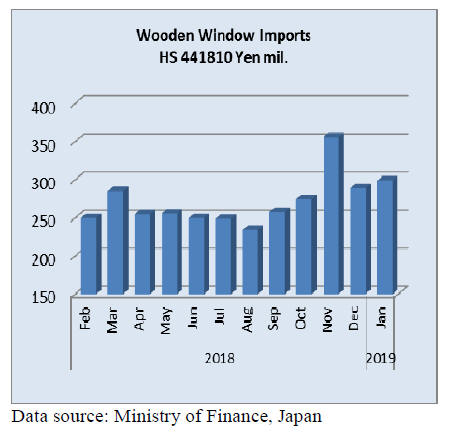
Wooden window imports
After falling sharply in December following a surge in
imports in November 2018 the value of imports steadied in
January coming in at around the average for the previous
year. Year on year, January 2019 wood window imports
(HS441810) rose 12% but were little changed from levels
in December 2018.
In January 2019 the top suppliers were China (33%), USA
(19%) Sweden (17%) and the Philippines (15%)
representing over 80% of the value of all shipments of
wooden windows to Japan.
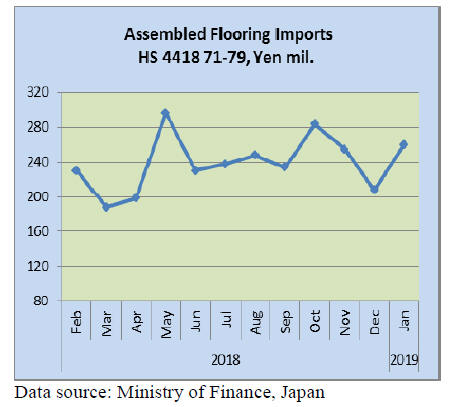
Assembled wooden flooring imports
Year on year the value of Japan¡¯s January 2019 imports of
assembled wooden flooring (HS441871-79) dipped 27%
but, month on month the value of imports rose 25%.
In January 2019 three products accounted for all wooden
floor imports, HS441873 (16%), HS 441875 64% and
HS441879 20%. As in previous months HS441875
accounted for most of the wooden floor imports with
shippers in China, Thailand and Indonesia accounting for
61%, 12% and 11% respectively.
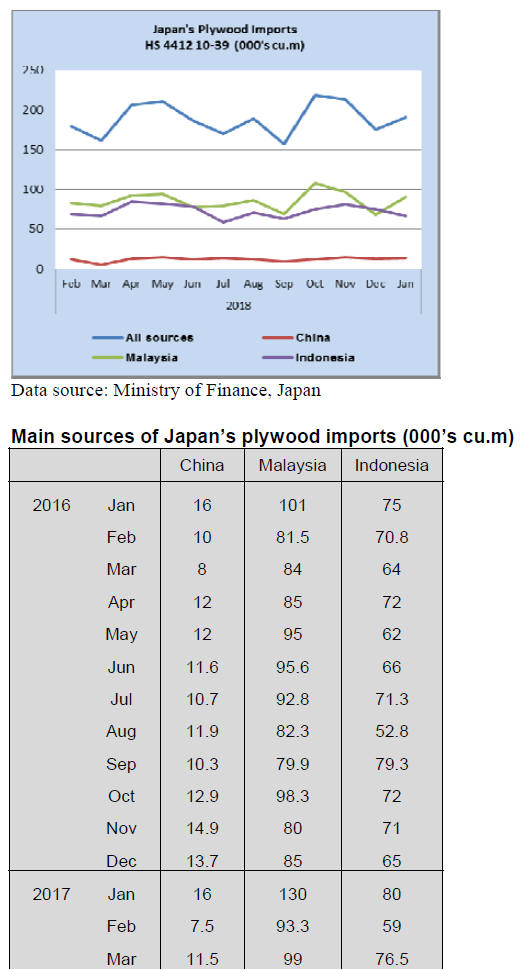
Plywood imports
As was the case in 2018, three supply countries continued
to account for over 85% of Japan¡¯s imports of plywood in
January 2019.Malaysia, Indonesia and China dominate
plywood imports but shippers in Vietnam are steadily
securing market share.
Year on year, the volume of Japan¡¯s January 2019 imports
of plywood (HS441210-39 were down 9% but compared
the volume of imports in December there was a steep rise
in January imports due mainly to a 34% rise in shipments
from Malaysia (68,000 cu.m in December 2018 to 91,200
in January 2019).
January shipments from China were little changed year on
year and month on month but Indonesian shipments were
down 17% compared th January 2018 and were down11%
compared to a month earlier.
HS441231 is the main category of plywood imports into
Japan accounting for over 80% of all arrivals in January
2019.
Trade news from the Japan Lumber Reports
(JLR)
The Japan Lumber Reports (JLR), a subscription trade
journal published every two weeks in English, is
generously allowing the ITTO Tropical Timber Market
Report to reproduce news on the Japanese market
precisely as it appears in the JLR.
For the JLR report please see:
http://www.nmokuzai.
com/modules/general/index.php?id=7
Import of wood products in 2018
The Japan Lumber Importers Association summed up
import of wood products in 2018. All the items except for
wooden board decreased for two straight years. New
housing starts in 2018 declined by about 2% in 2018 so
that the demand for building materials decreased.
By items, lumber import decreased by 5.1%. This is the
first decline after three years. Particularly European
lumber import dropped by 9.2% and Canadian lumber
dropped by 6.3%.
Reason of decline of European lumber is adjustment of
oversupply in 2016 and 2017. Total of 380,000 cbms of
lumber decreased from both Europe and North America.
Russian lumber supply recovered and Chilean lumber
supply increased by 15.6% with 330,000 cbms, the highest
volume in last ten years.
Log import decreased by 1.2%.Main source of North
America decreased by 2%. Reasons are users in Japan
shied away from high prices and import reduction by drop
out of one large Douglas fir sawmill.
Radiata pine logs increased from New Zealand. South Sea
hardwood logs also increased despite log export ban by
state of Sabah, Malaysia as supply source moved to PNG.
Decline of Russian log import continues.
Plywood is the largest in imported finished products. The
volume is steady despite log supply tightness in producing
countries, which proves solid demand in Japan. MDF
import was 612,000 cbms, the record high import by
declining domestic supply and growing demand. Both
import of OSB and particleboard increased. Import of
laminated lumber was curtailed in 2018 to adjust over
import in 2017.
Increasing use of domestic wood
The Wooden Home Builders Association of Japan
disclosed result of the survey about use of domestic wood
for wooden houses through house builders and precutting
plants. The survey is made in every three years since 2005
by sending out questionnaires. This is the fifth survey.
160 member of housing companies responded, which built
62,412 units. 66 precutting companies responded, which
supplied 117,023 units in 2017. Percentage of domestic
wood use by house builders in 2017 was 45.4%, 13.1
points more than previous survey.
By members, more than 50% is domestic wood are sill,
stud, girder, floor sheathing, wall and roof. Use of
domestic wood by precutting plants is 33%, 1.5 points up.
Sill and structural panel are two items with over 50% of
domestic wood.
Use of domestic wood increased for post, sill, standard
lumber and plywood but use for other members decreased.
Remarkable change is use of laminated lumber from solid
wood lumber on both house builders and precutting plants.
House builders¡¯ use of lumber is 32%, 9.6 points less than
2014 survey while laminated lumber is 63.9%, 7.9 points
up. Precutting plants¡¯ use of lumber is 33.7%, 25.8 points
less while laminated lumber is 63.4%, 24.8 points more.
By species, increase use of cedar and Douglas fir
laminated lumber is apparent. House builders use 7.6% of
cedar laminated lumber, increase of more than 1.7 times.
Precutting plants use 5.3% of cedar laminated lumber,
increase of more than 2.5 times. Increase use of Douglas
fir laminated lumber is result of tight supply of European
redwood laminated lumber in 2017.
Wood products export in 2018
Total wood export in 2018 in value was 35.069 billion
yen, 7.4% more than 2017 and this is the first time that the
value exceeded 35 billion yen since 1977. Log export was
1,157,438 cubic meters, 19.3% more than 2017 and the
first time to hit over one million cbms.
As destination, China took 948,339 cbms, 22.2% more,
this pushed total up in 2018.
As to lumber export, total was 145,995 cbms, 12.3% more.
22,703 cbms for the U.S.A., 74.6% more and 11,403 cbms
for Taiwan P.o.C, 78.5% more and they are leaders of
lumber export.
Log export climbed sharply for three years since 2013 then
it paused in 2016 but it increased sharply in 2017 again
and high pace continued in 2018. The volume for China is
large factor of increase then 74,620 cbms for Taiwan
P.o.C, 34.7% more and 9,087 cbms for Vietnam, 64.7%
more also contributed the increase.
By species, cedar logs were 838,784 cbms, 29.4% more
while cypress logs were 132,352 cbms, 6.6% less. China
bought 697,731 cbms of cedar logs, 24.5% more and
83,466 cbms of cypress logs, 40.1% more.
Korea took 69,143 cbms of cedar logs, 85.9% more then
38,666 cms of cypress logs, 48.3% less. One possible
reason of this decline of cypress for Korea is that logs
exported to China are processed and exported to Korea.
Lumber exporst of cypress to Korea also dropped by 4.5%.
Cedar lumber export to the U.S.A. continues expanding
since 2016 for exterior use like fencing and decking. The
U.S.A. is now the third largest lumber export destination
next to China and Philippines.
Log export to Taiwan P.o.C is decreasing while lumber
export is increasing.
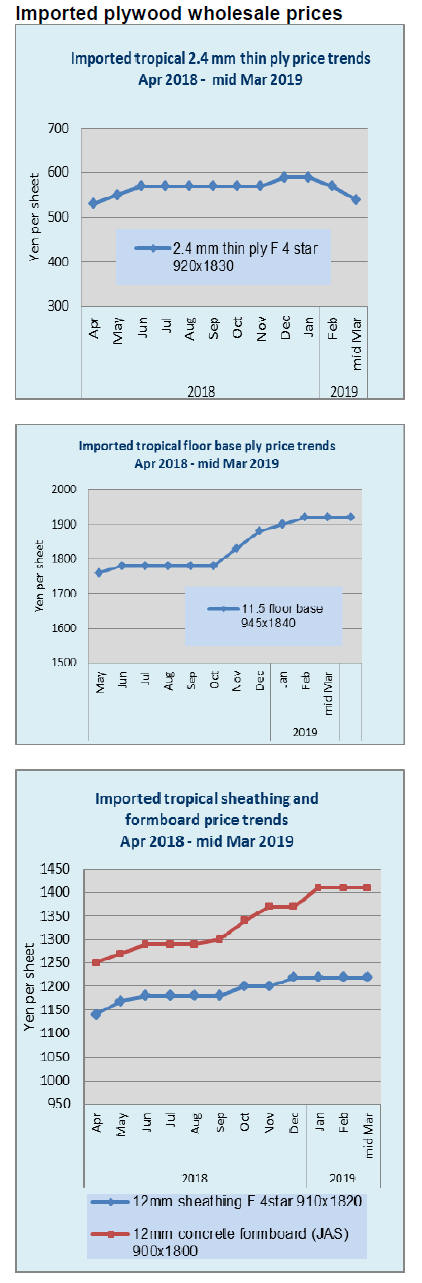
Plywood supply in 2018
Total plywood supply in 2018 was 6,139,800 cbms, 0.4%
more than 2017. Domestic plywood production was
3,216,700 cbms, 0.2% more out of which softwood
plywood was 3,088,100 cbms, 0.8% more.
Imported plywood was 2,923,000 cbms, 0.7% more.
Import plywood has been less than three million cbms for
last four years. Share of domestic supply was 52.4% and
the domestic supply surpassed the imports for three
straight years.
In domestic production, structural plywood was 2,861,300
cbms, 2.2% less than 2017 while non-structural panel
production exceeded over 200 M cbms for the first time.
Shipment of softwood plywood was 3,046,100 cbms, 0.3%
less in which structural panel was 2,824,100 cbms, 3.1%
less. Shipment of softwood plywood exceeded three
million cbms for two straight years. Despite startup of new
plywood mill in 2018, total production did not increase
because plywood mills stopped overtime and week end
operations to improve working conditions for securing
young workers.
Imported plywood supply varies by source. Malaysian
supply was 1,062,000 cbms, 10.8% less than 2017 while
Indonesia was 977,500 cbms, 11.4% more.
Chinese supply was 642,000 cbms, 1.9% less. Indonesian
supply was over 900,000 cbms after two years while
Malaysian supply was less than 1,100,000 cbms. Because
of high export prices by supplying countries, total volume
of imported plywood will drop this year.
South Sea (tropical) logs and Lumber
Total import of South Sea logs in 2018 was 153,407 cbms,
4.5% more than 2017. Logs from Malaysia decreased after
Sabah banned log export since May last year but PNG
covered shortfall of Malaysia with 76,394 cbms, 64.5%
more than 2017. Log prices in Japan are unchanged
because log prices in PNG are lower than Malaysian log
prices.
Inventory of laminated free board has been dropping so
orders to supply side started increasing, not because of
demand recovery but by dropping inventory in Japan.
Import of Chinese red pine lumber and Indonesian
mercusii pine is getting low so the suppliers prices are
firm.
Next generation housing point system
The Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport newly
created next generation housing system to ease rush-in
demand for housing before the consumption tax is raised
from present 8% to 10% in October 2019. This gives merit
to buy house after October. This budget is about 130
billion yen and has been approved in December 2018 so
the amount is allocated in 2019 budget.
The system is to give points, which can be used to
purchase home appliances when energy saving, earthquake
proof, barrier free houses are built. Maximum points given
is 350,000 yen for newly built house or 300,000 yen for
renovation. Contract needs to be made by March 31, 2020.
Also deduction period of housing loan tax is extended
from 10 years to 13 years. Also tax free limit of gift tax is
increased from 1.2 million yen to 3.0 million yen. Tax
deduction on housing loan of 1% of loan balance at the
end of the year is refunded. For instance loan amount is 30
million yen to buy 30 million yen house, total tax
deduction amount for ten years is about 2.69 million yen.
2% tax on 30 million yen is 600,000 yen so if loan amount
is large, 2% tax increase is easily offset by this measure.
Benefit on new house purchase is increased from 100,000
yen to 400,000 yen for people with income of 7.75 million
yen, which was 5.1 million yen when consumption tax rate
is 8% so it is better to buy house after the tax rate is
increased to 10% for people with income of less than 7.75
million yen.
Last measure when the tax rate was increased was mainly
designed by the Ministry but this time, Liberal Democratic
Party strongly promoted so this is politically promoted
deal.
|